How to Install the Platform and Plugins
Strider Installation
This guide walks you through the installation of Strider on your own infrastructure. Since there are many operating systems out there, we're going to keep this guide as universal as possible. We outline required technologies and you have to install them on your own.
Requirements
Strider is build on top of Node.js and MongoDB as data store. Since it integrates to services like GitHub, GitLab and Bitbucket you need to have git installed as well.
Installation
Before starting the installation process, please install the required technologies. Afterwards, go ahead and follow the steps to install a basic platform and later on change the configuration to connect against a MongoDB with authentication enables. Of course you can use a remote database like one provided by MongoLab.
Create a Strider User
Keep an eye on security if you run an internet-reachable Strider deployment. You should create a separate operating system user with restricted access for Strider. Unix-systems have the system function addUser <username> which provides the ability to quickly add a new system user.
Clone Strider Repository
Now you need the Strider source code. You can head over to Strider's GitHub repository and choose your desired clone url or just copy the command below.
git clone https://github.com/Strider-CD/strider.git && cd strider
Go to the folder of your choice and clone the Strider code to your machine.
Install Strider
Verify all requirements are installed on your machine. From here it's just one command to get Strider installed.
rush install
Strider uses the Node Package Manager to install required dependencies and set up a default platform. If there went something wrong during the installation, NPM will output the errors. Strider points to an error where issues with permissions occur installing global modules. In case you have those troubles, set the global modules directory to ~/npm by npm config set prefix ~/npm. Additionally, you have to add ~/npm/bin to your PATH environment variable.
The default configuration should be fine to test if everything was installed correctly. Start Strider
cd aps/strider
# either
npm start
# or
bin/strider
This way requires you run a local MongoDB instance without authentication. If you use a MongoDB instance with authentication turned on (we recommend that!), the start up command will print out connection errors with MongoDB. You can follow the steps below to set up Strider correctly for MongoDB with activated authentication.
Running Strider with Activated MongoDB Authentication
We totally recommend to run MongoDB with authentication. You need to create a MongoDB user, a database and grant the user access to the database.
Create Strider User in MongoDB
Connect to MongoDB as an Mongo admin. Authenticate against your admin database (or what authentication source you use). Now switch to the database you want to use for Strider. The example snippet below uses strider for user and database name.
# if not running on default port 27017, pass the MongoDB port number
mongo --port <port>
## Mongo CLI
> use admin
> db.auth('admin', 'adminpassword')
1
use strider
db.createUser({user: "strider", pwd: "striderpw", roles: [{role: "dbOwner"}]})
The snippet above creates a new user called strider within the database called strider as well. Futher we assign our strider user the dbOwner role to have correct access rights to modifiy the database.
Pass Database URI to Strider
Strider uses Mongoose for database connection and operations. We need to pass a connection string to Strider when running MongoDB with authentication. You can use the DB_URI environment variable to pass it to Strider.
Change the MongoDB port if you run MongoDB on another port than the default 27017.
DB_URI="mongodb://strider:striderpw@localhost:27017/strider" npm start
For now it's important to know that DB_URI configures a custom MongoDB connection string.
Start Strider in Production
For production environments, please use the NODE_ENV environment variable to set Strider into production mode. By default, Strider starts into development mode and you need to make the switch
NODE_ENV=production npm start
How to Install Plugins
Strider provides a command line wrapper to install plugins from the ecosystem index. If you don't want to crawl through the command line, you can use the web UI and install new plugins via Strider's admin panel.
Install Plugins in Strider Admin Panel
The admin panel displays all plugins listed in the ecosystem index. You can (un)install them freely within the browser.
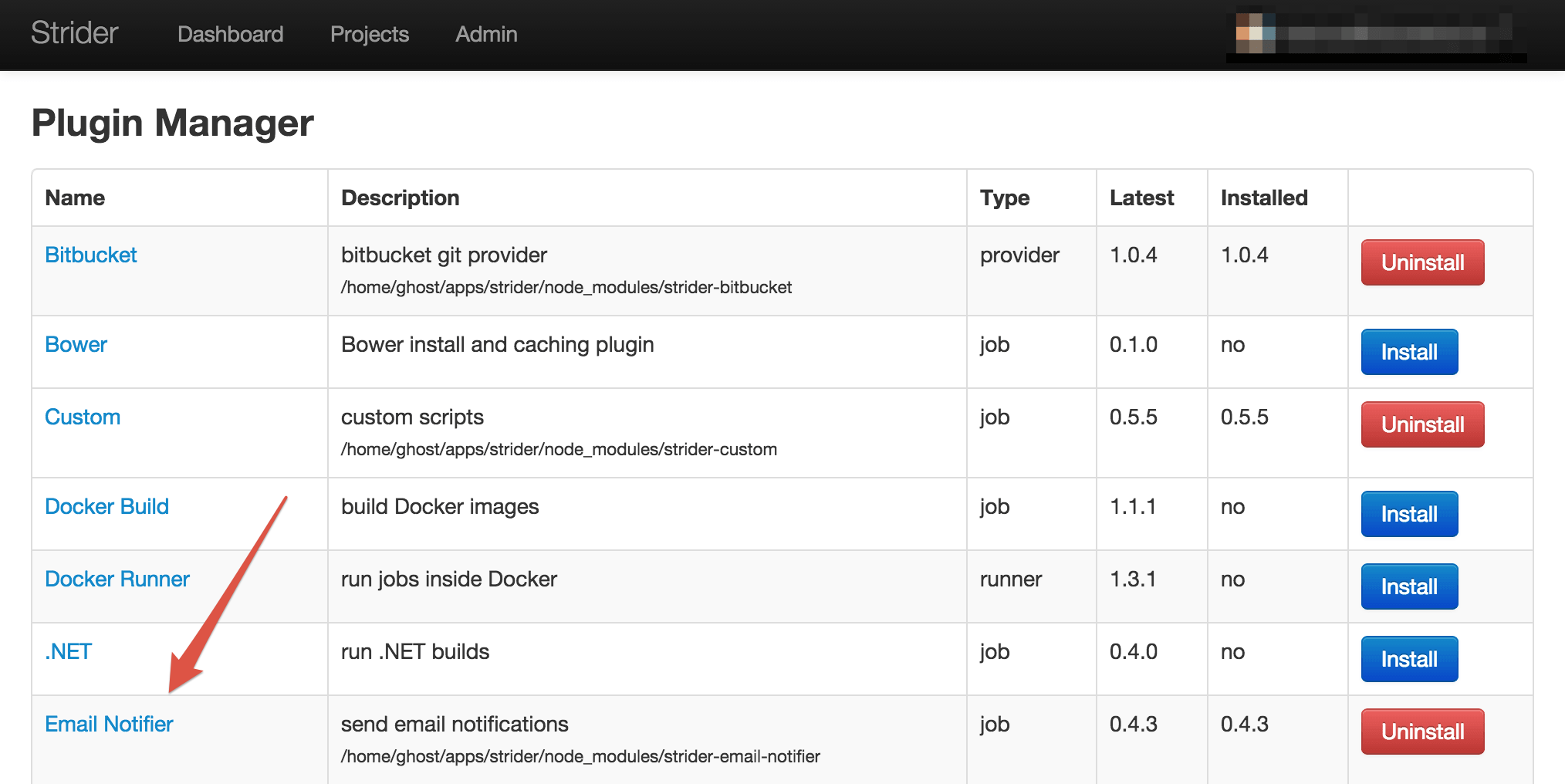
The plugin overview also prints out the currently installed and latest plugin version. In case you've installed outdated plugin, you can update them directly from web as well.
Install Plugins via Command Line
You love the command line? Don't worry, you're covered and can install the plugins listed in the ecosystem index right away.
bin/strider install <plugin-name>
Strider first checks if the plugin is already installed. If not, it looks in the index to find the pluins GitHub repository. Afterwards, it clones the plugin repository and installs via npm.
Another way to install new plugins is to do so directly with npm. Just navigate to Strider's base repository and install the desired plugin. This way you rely on third party addons which may not work correctly with Strider and isn't approved by the Strider team.
There are some Strider addons not listed in the ecosystem index and you still want to install them? Don't worry, go ahead an install using npm. In case you recognize any misfunction just remove the trouble causing plugin.
npm install <plugin-name>
You need to restart your Strider server to activate newly installed plugins.